Sizing CC/BM buffers: The cut and paste method
The Critical Chain/Buffer Management (CC/BM) approach uses project and feeding buffers to add safety time to the project baseline schedule and to guarantee the timely completion of the project with a high probability. Buffers are sized according to the properties of the path or chain feeding those buffers, such as the length of the path, its total variance or the number of activities it contains. This article describes the cut and paste method, which is probably the simplest method to determine the size of the project and feeding buffers and is solely based on the activity duration of the chain merging in the buffer.
Figure 1 displays a project network with 8 activities. The numbers above each node are used to refer to the aggressive activity durations while the label below the node refers to a renewable resource that is required to perform the activity. The renewable resources A, B, C, D and F have an availability of one, while the renewable resource E availability is restricted to two units. The schedule contains three time buffers and one resource buffer. One project buffer is added to protect the critical chain S - 2 - 6 - 8 - E and two feeding buffers FB4-6 and FB7-8 are added to protect the feeding chains 1 - 4 and 3 - 5 - 7, respectively. The resource buffer RB is added to assure that resource B will be available on time to start with activity 6. More information on the determination of these buffers can be found at “Critical Chain/Buffer Management: Adding buffers to a project schedule”.
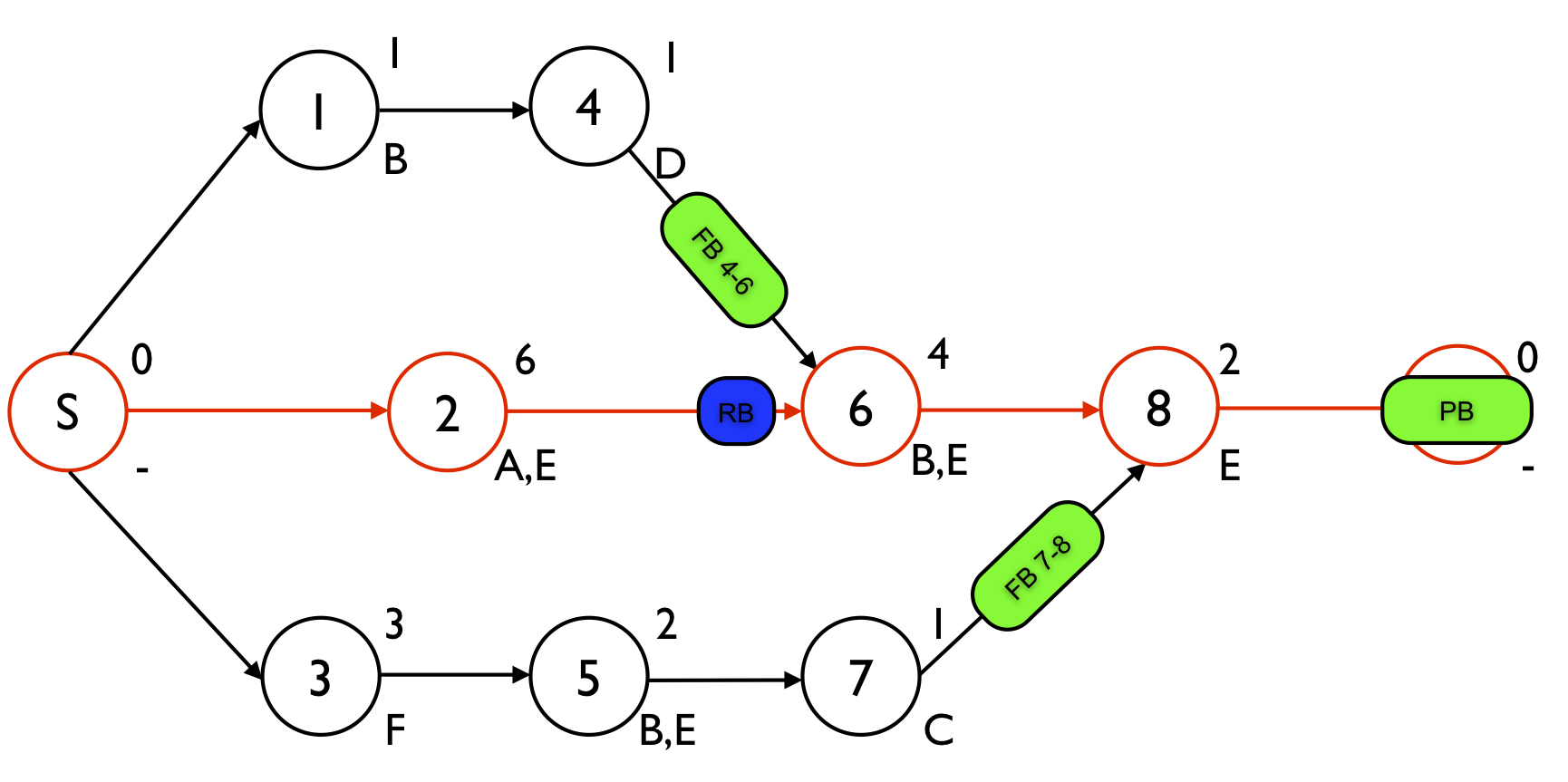
- Project buffer: 50% of (6 + 4 + 2) = 6
- FB4-6: 50% of (1 + 1) = 1
- FB7-8: 50% of (3 + 2 + 1) = 3
© OR-AS. PM Knowledge Center is made by OR-AS bvba | Contact us at info@or-as.be | Visit us at www.or-as.be | Follow us at @ORASTalks


